MIPSI Technique For Spine Disc Problem
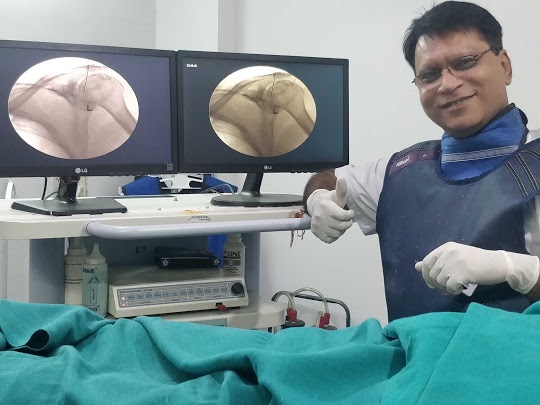
Hello friends here I am dr Sanjay Sharma interventional pain physician from JPRC Neuro Spine Centre Jaipur Rajasthan India,as my two decades experience in spine intervention.
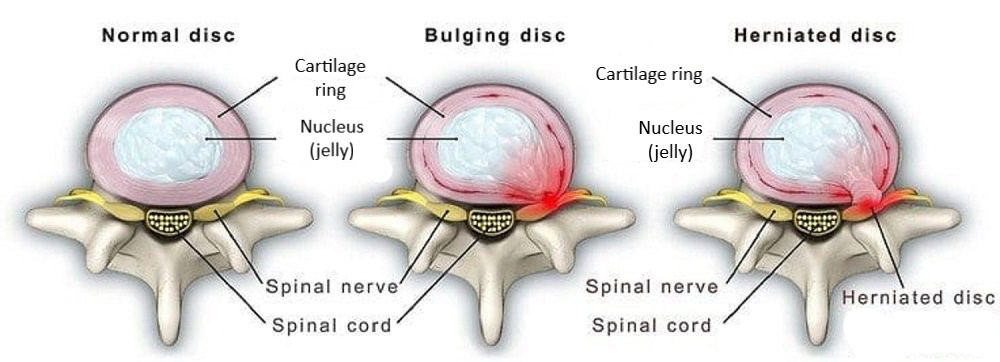
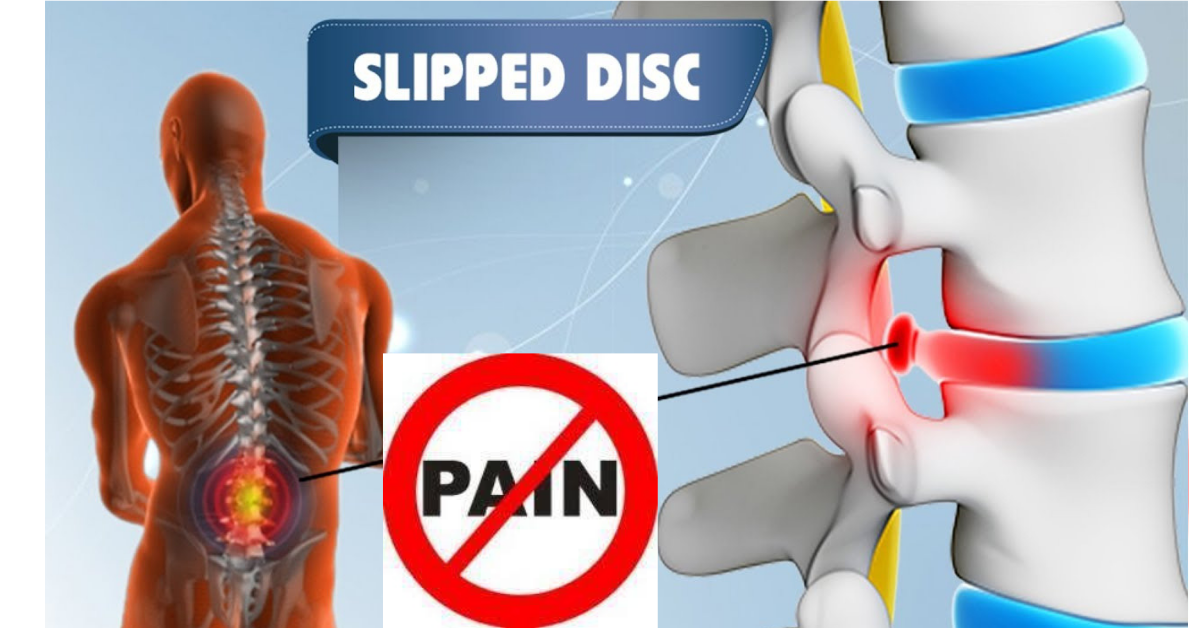
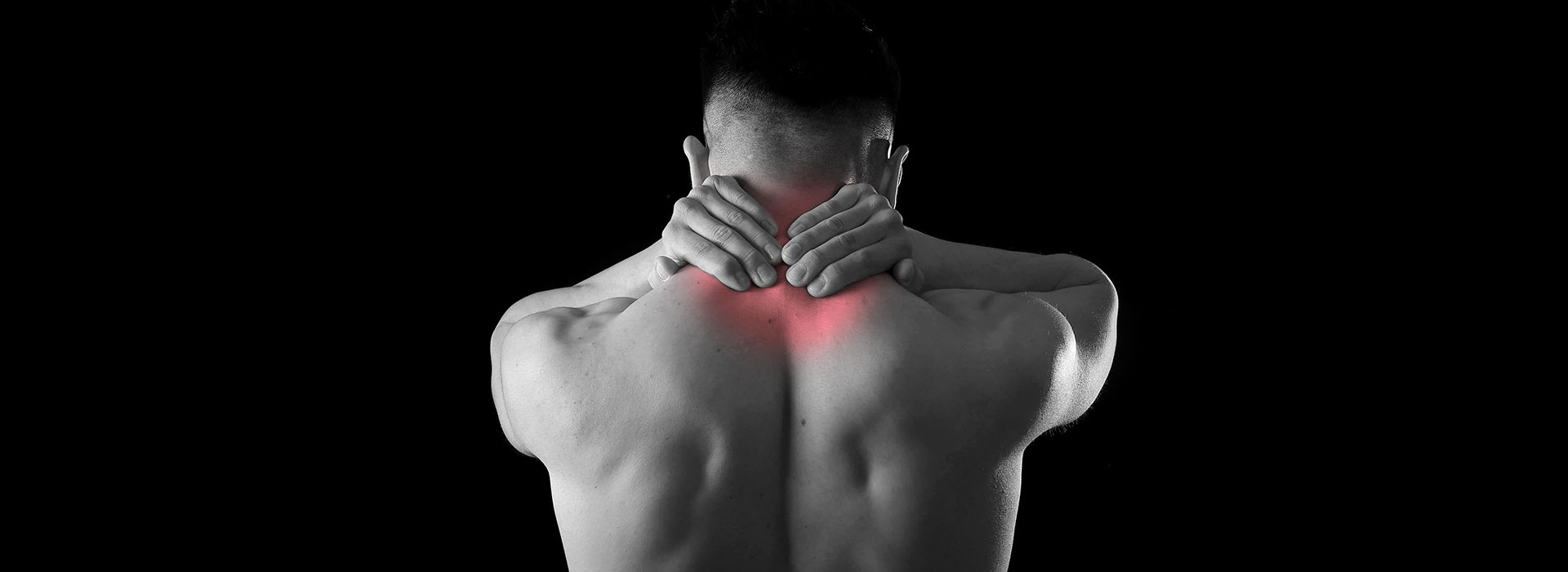
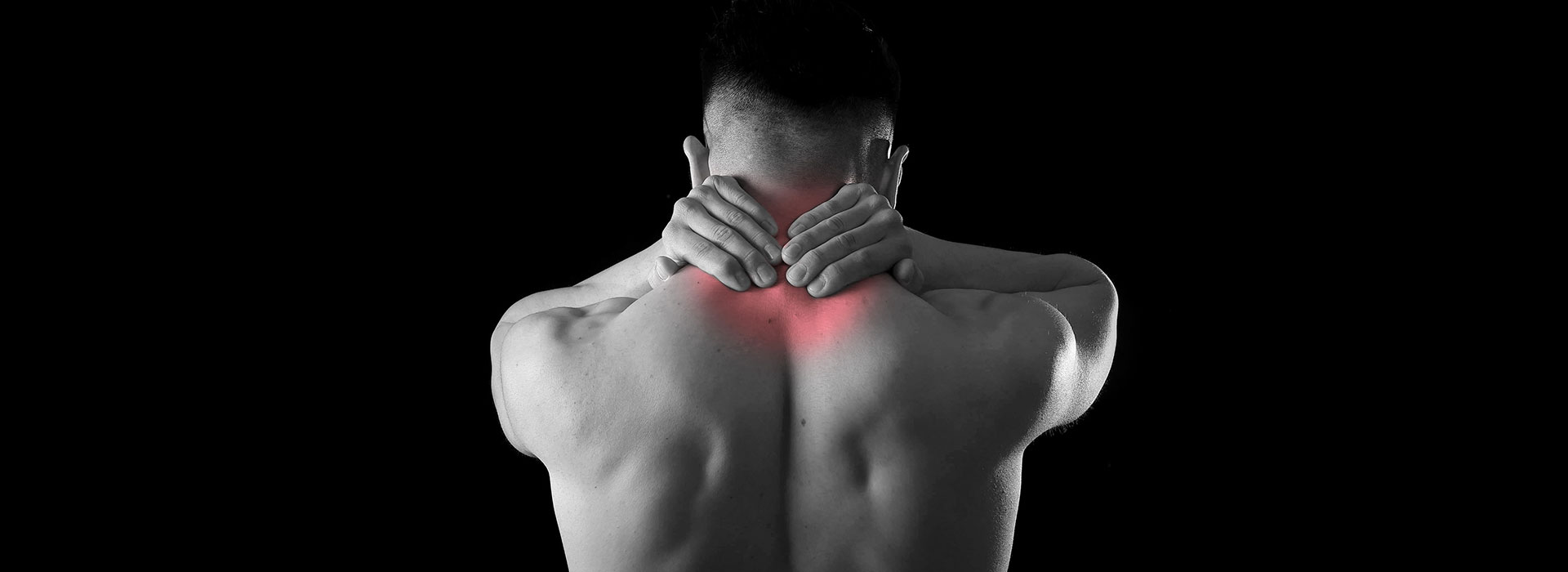
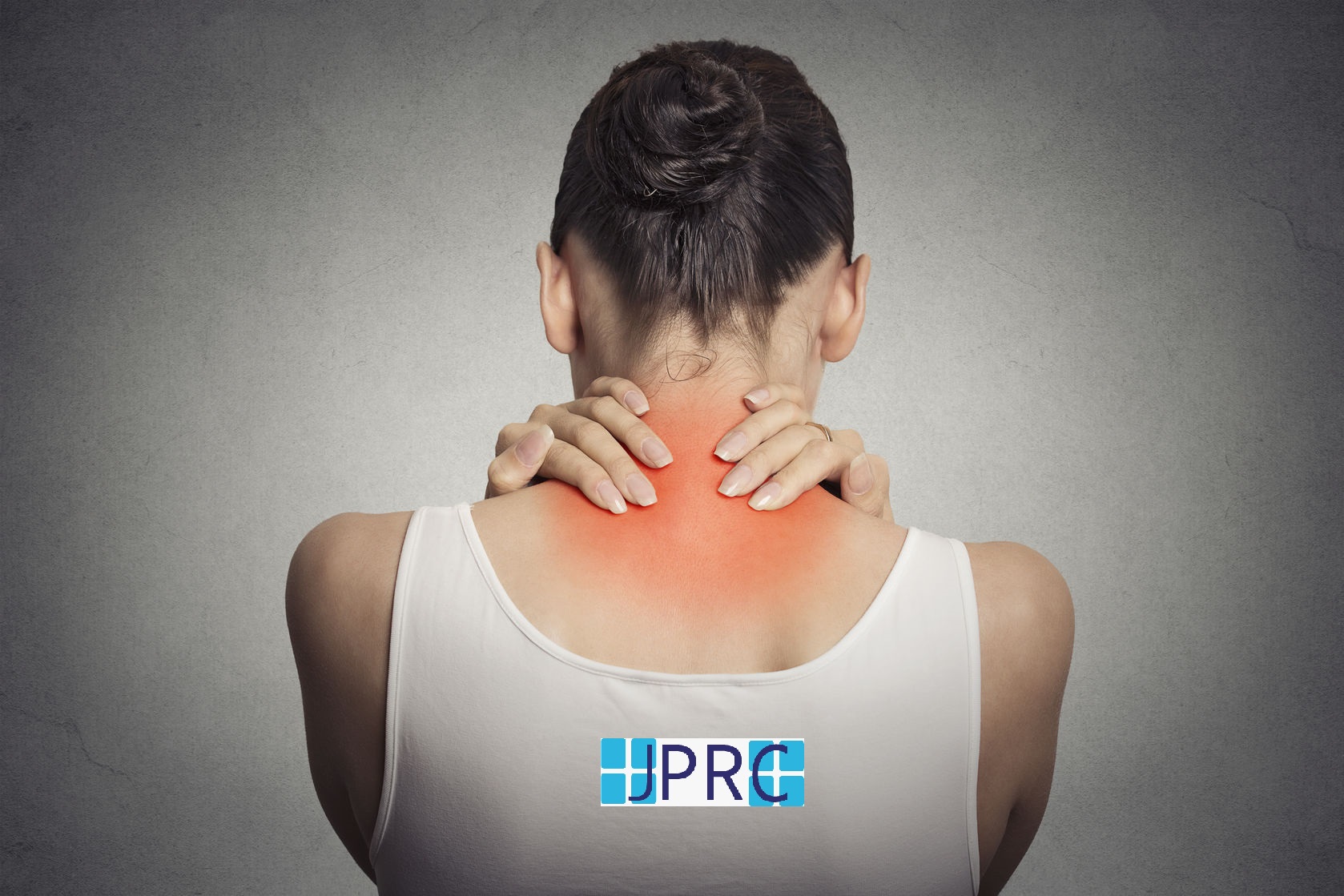
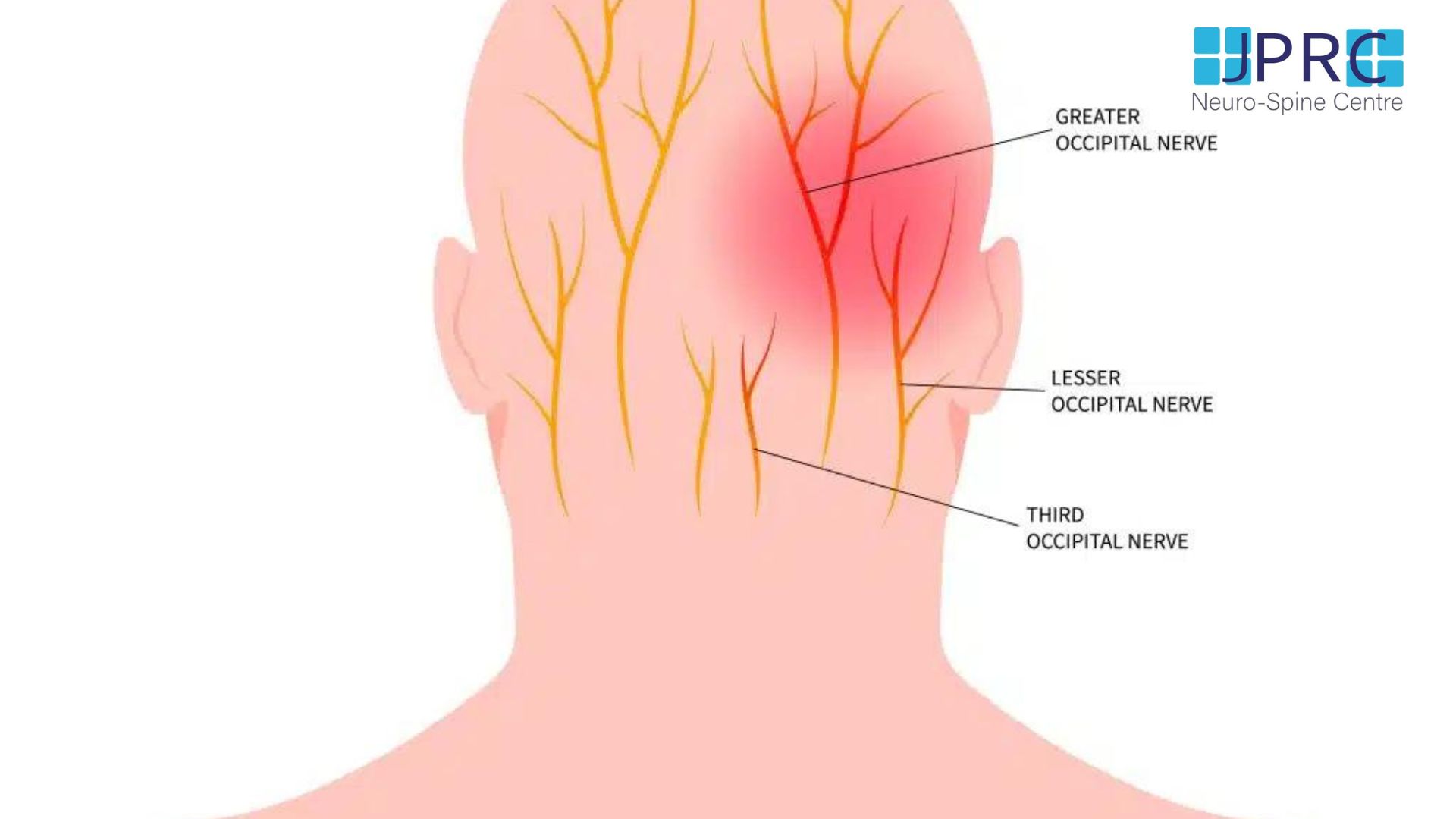
How to save you from conventional spine surgery from disc related pathology like disc bulging, protrusion and Annular tear etc
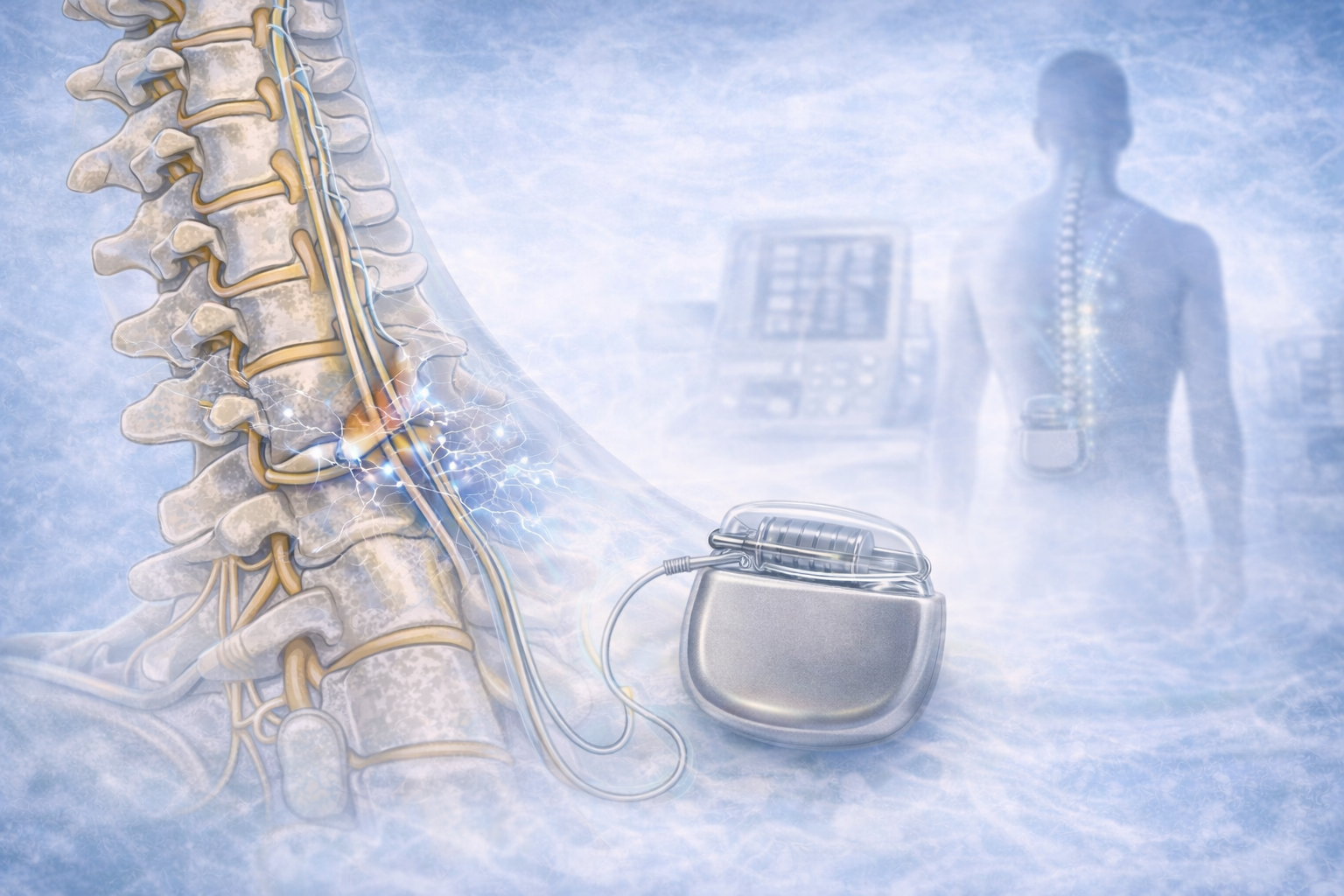
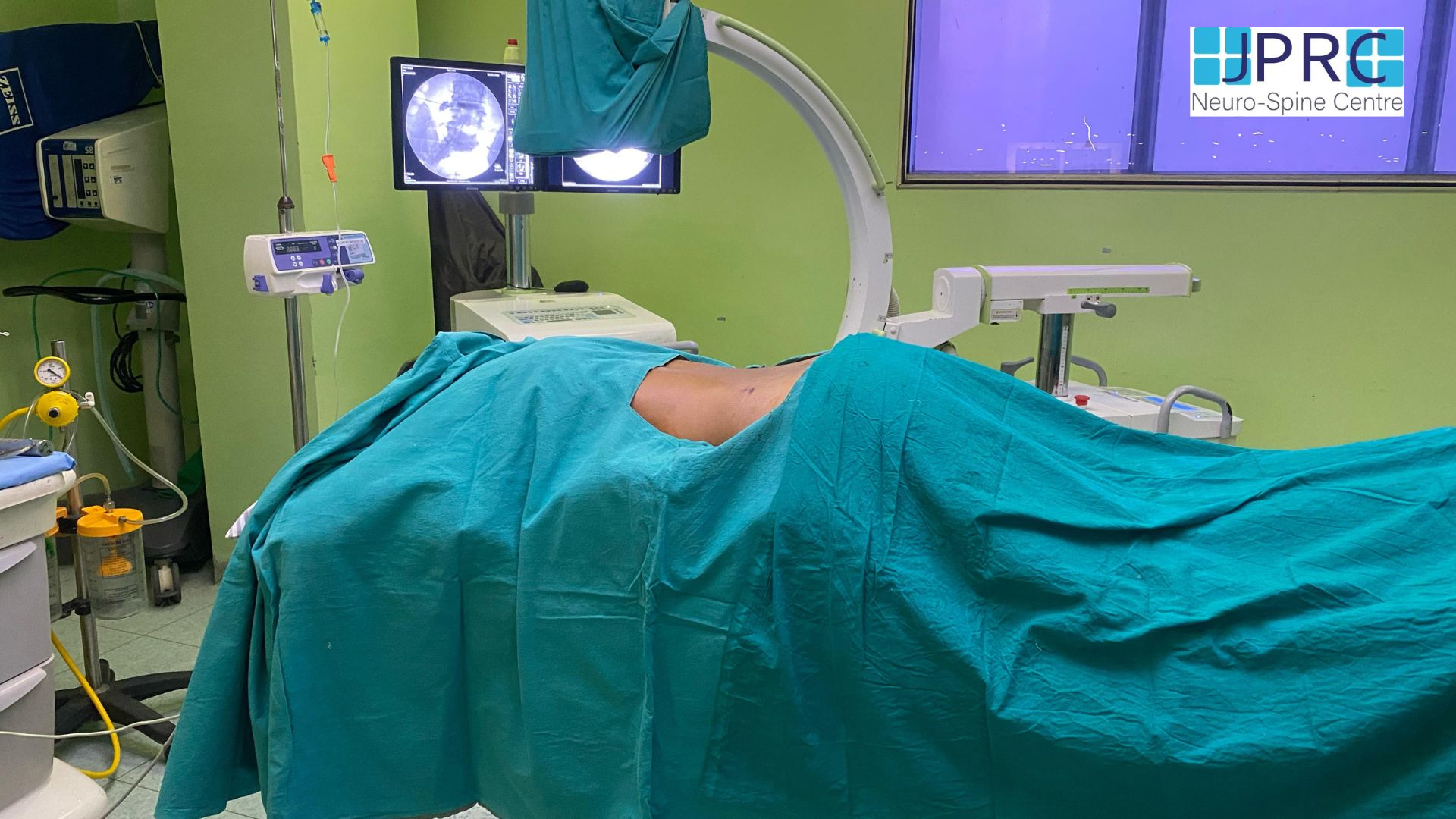
Here's a brief write-up on intradiscal pain intervention: MIPSI technique (minimal invasive pain and spine intervention)
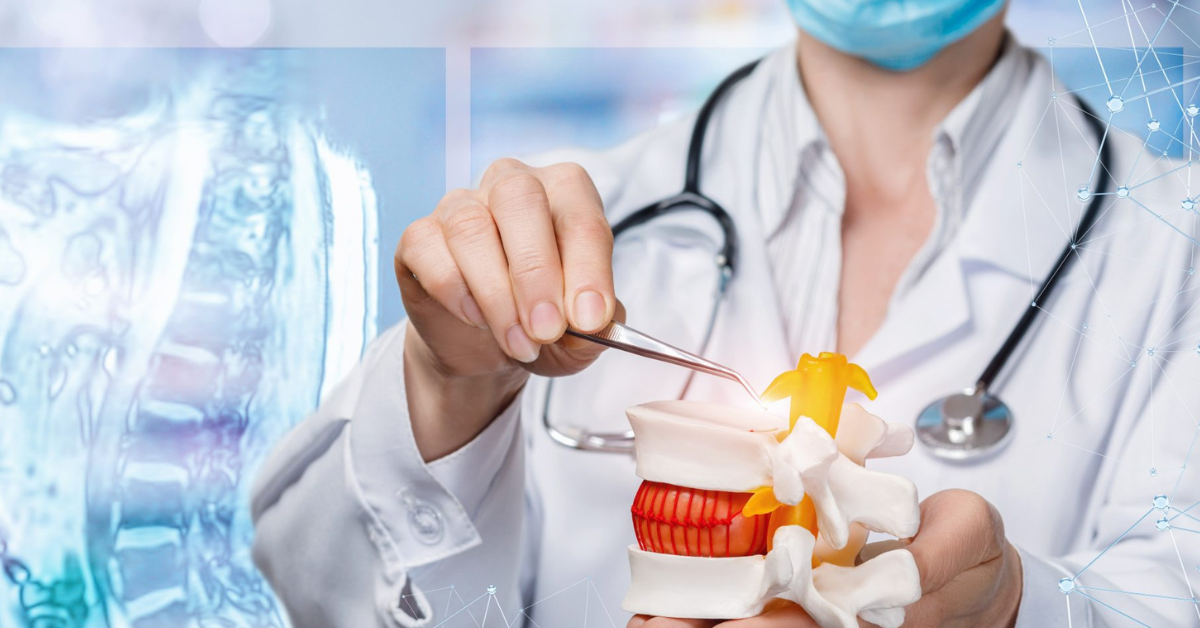
Intradiscal Pain Intervention: Techniques and Considerations
Introduction:
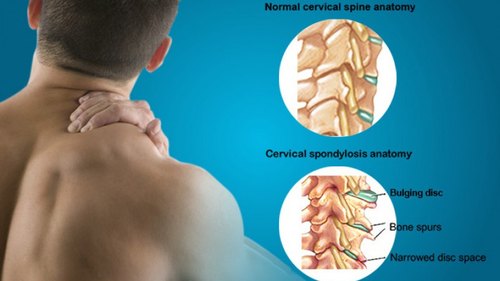
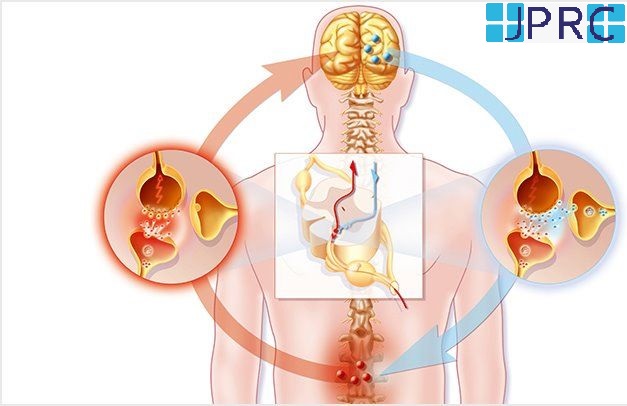
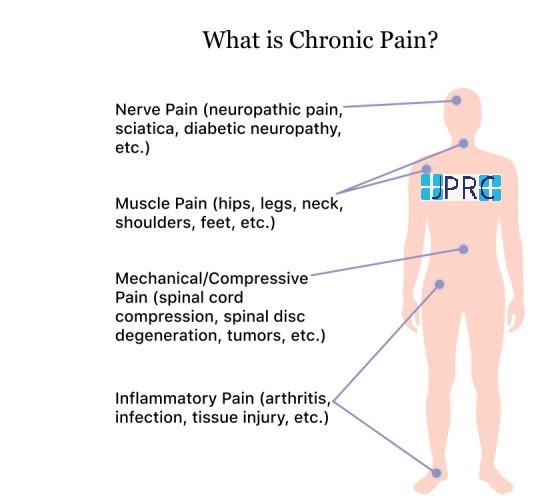
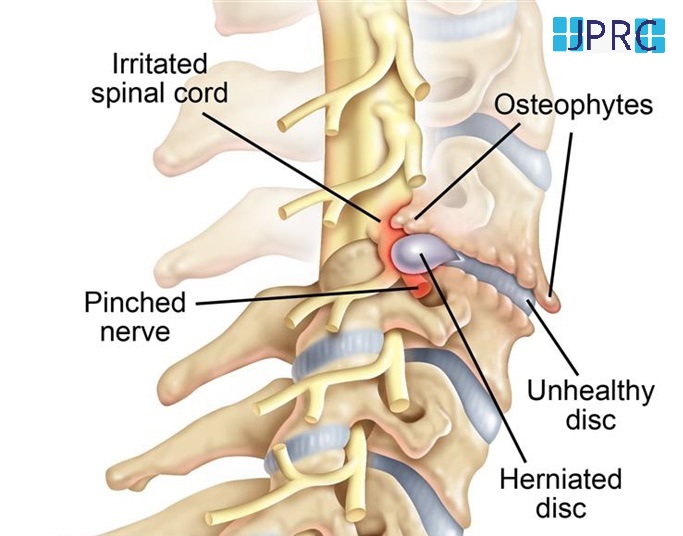
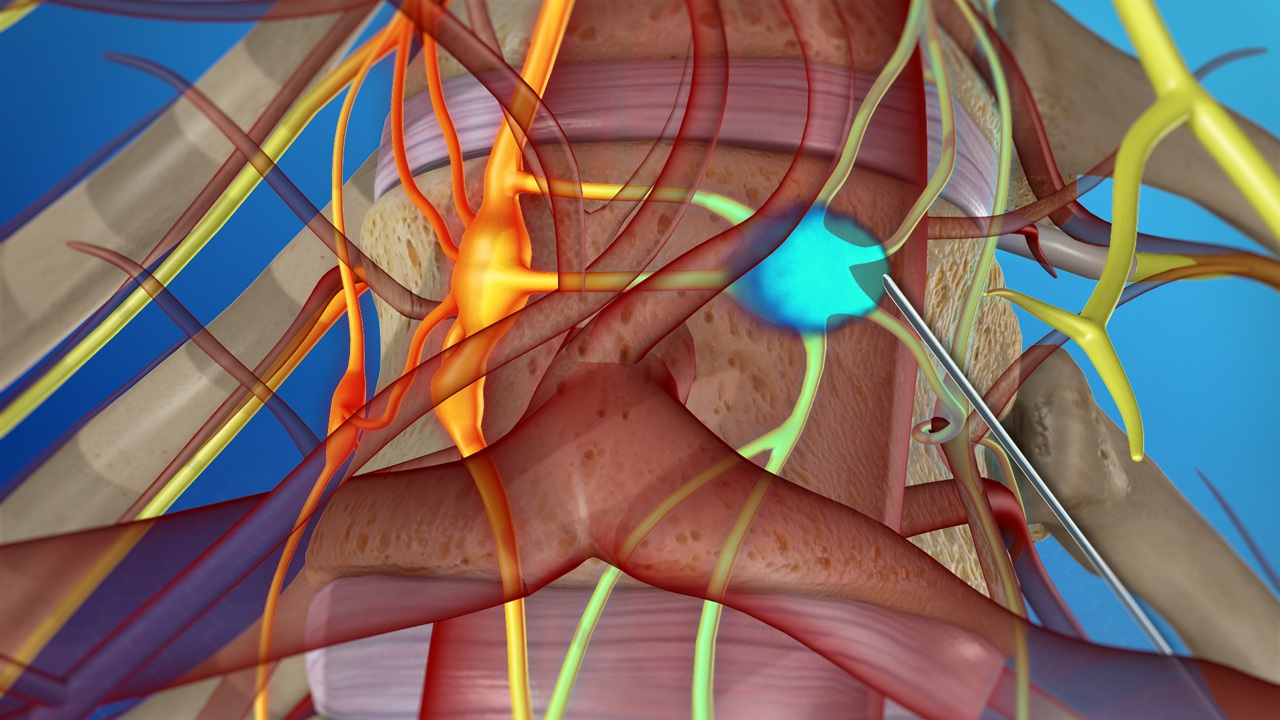
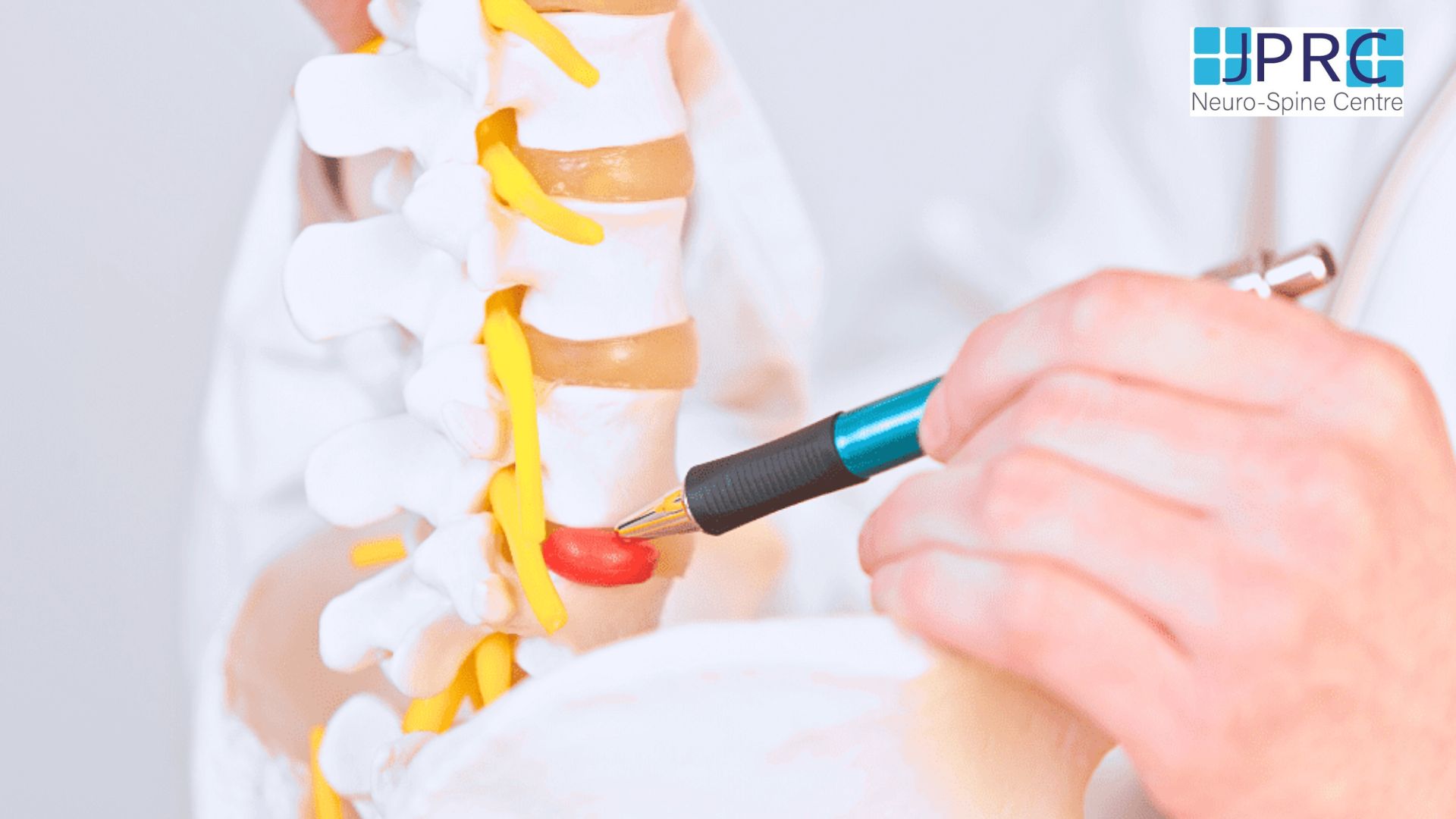
Intradiscal pain intervention involves various techniques aimed at alleviating pain originating from intervertebral discs. These procedures target specific areas within the disc to reduce inflammation, improve structural integrity, and alleviate associated symptoms.
Techniques:
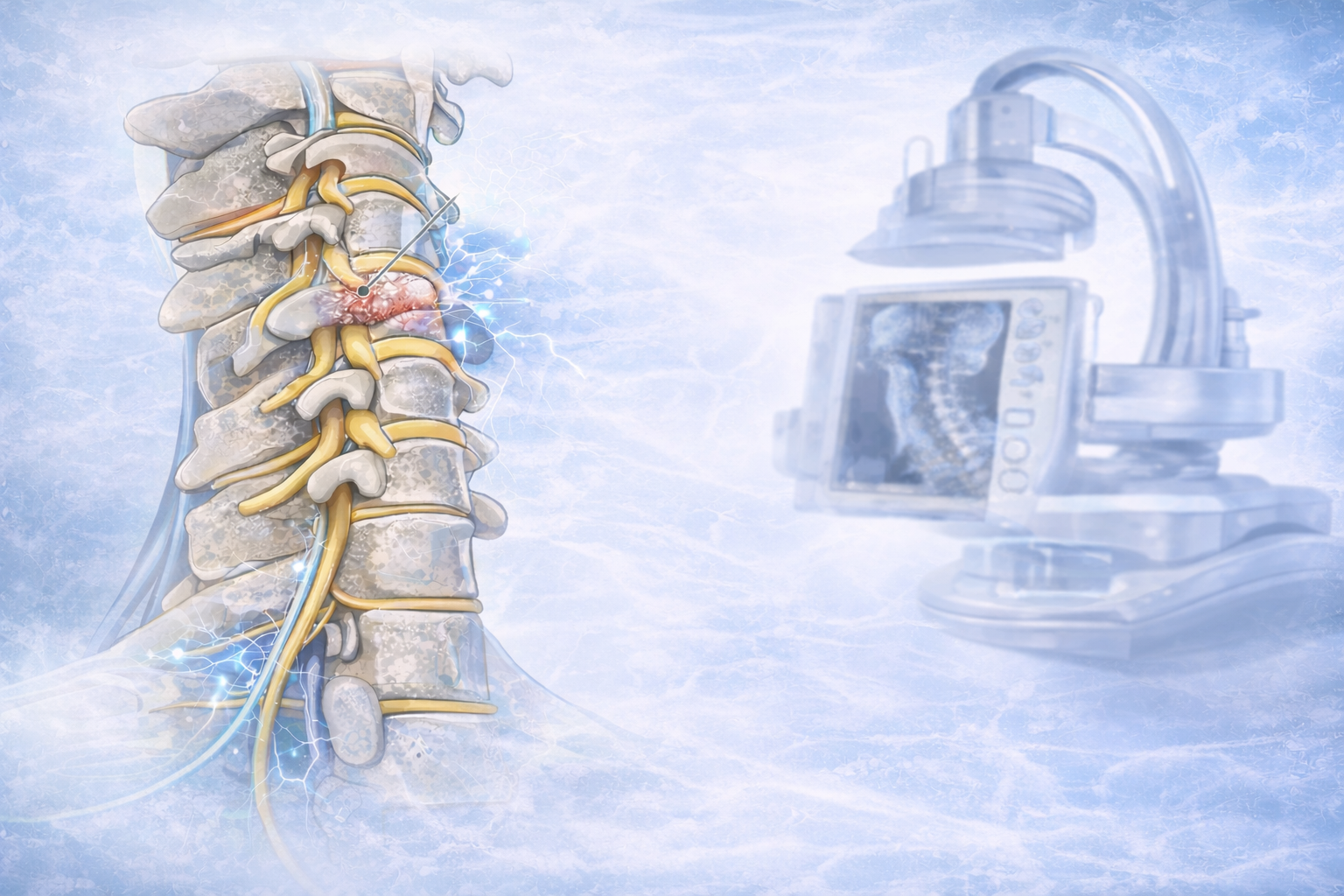
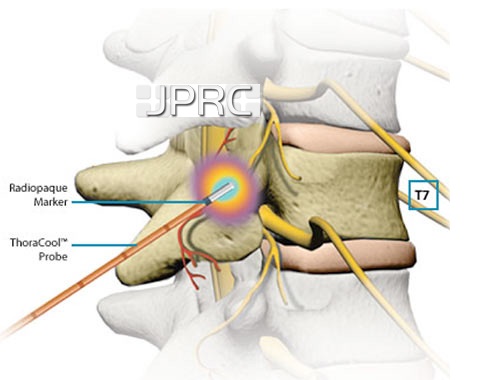
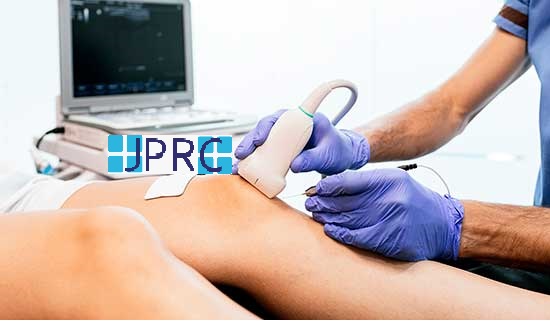
1. Intradiscal Electrothermal Therapy (IDET): IDET involves the application of controlled thermal energy to the affected disc under fluoroscopic guidance. The heat aims to denature pain-inducing nerve fibers and promote collagen retraction, thereby stabilizing the disc and reducing pain.
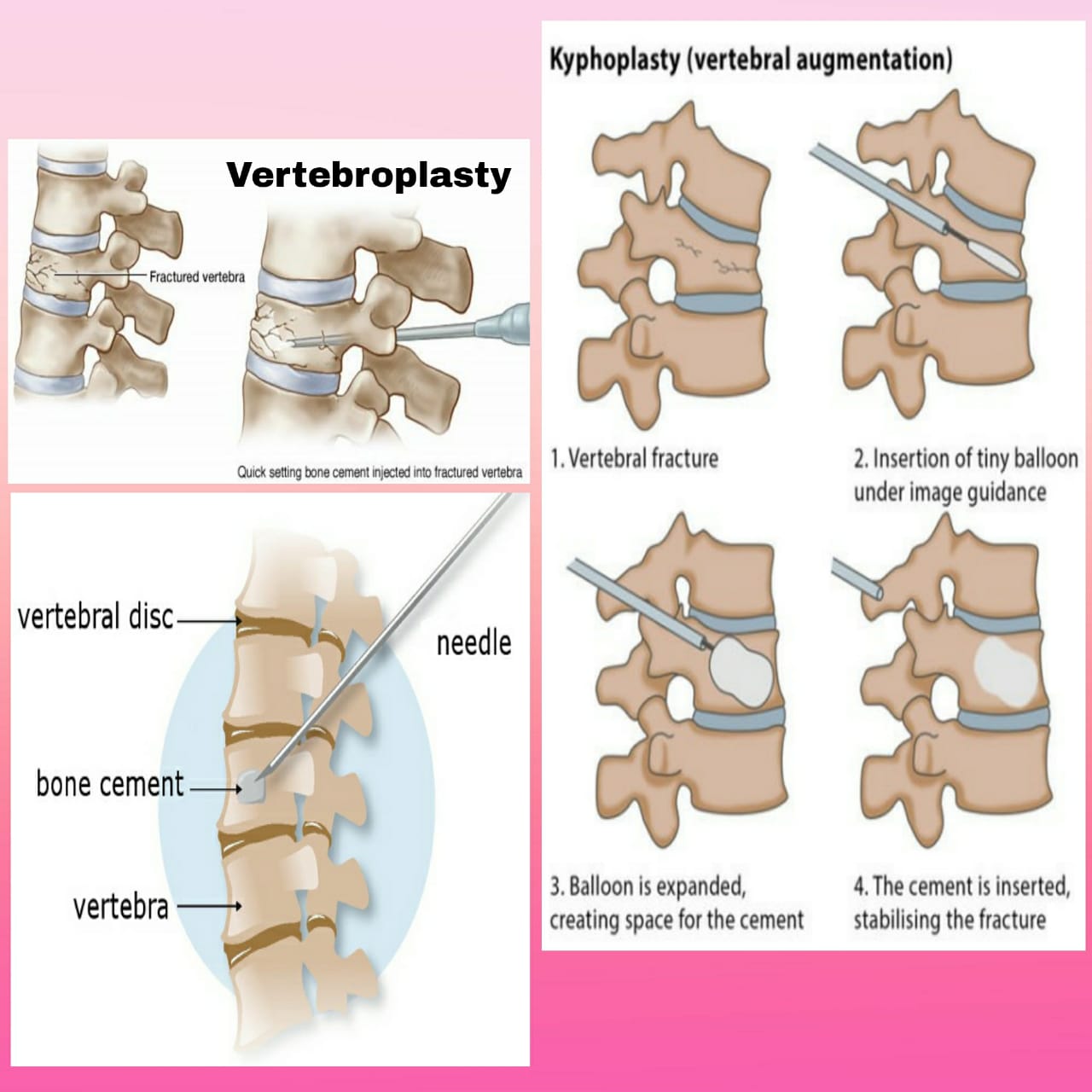
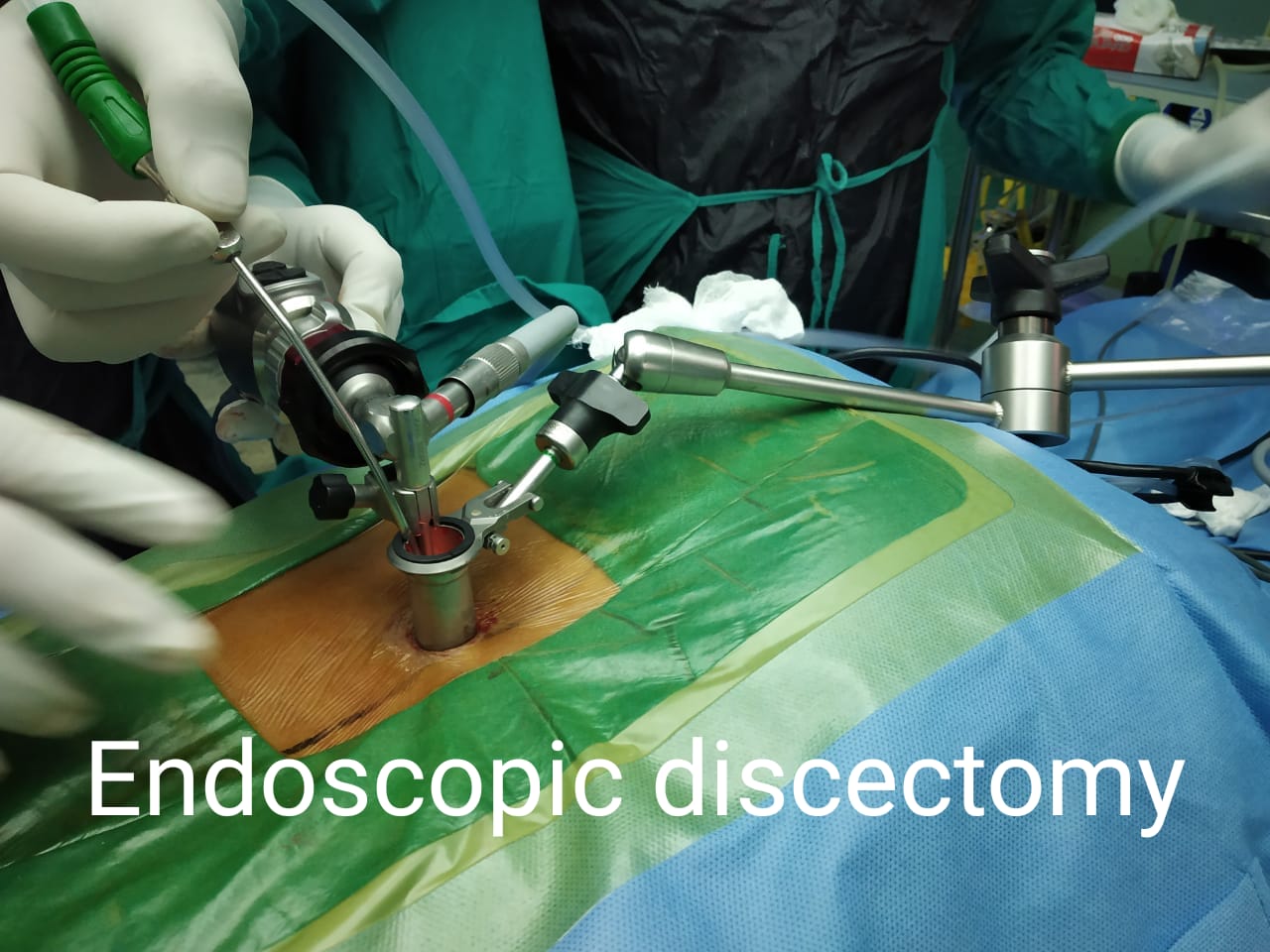
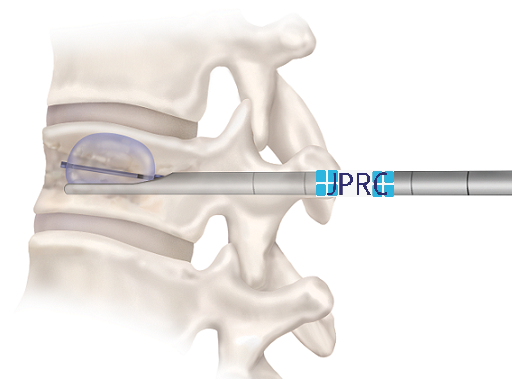
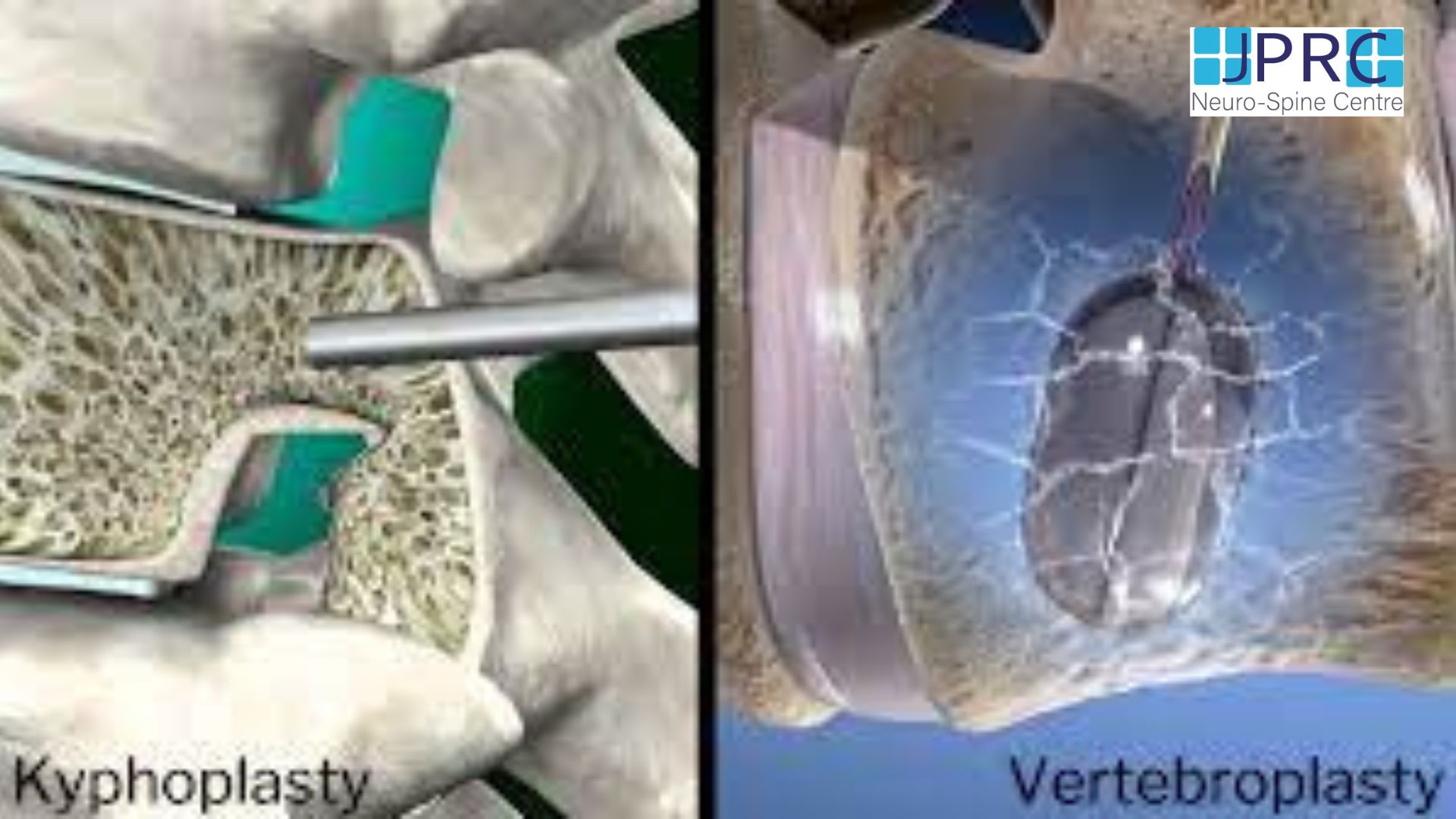
2. Percutaneous Disc Decompression (PDD):PDD techniques, such as nucleoplasty or coblation, utilize minimally invasive procedures to remove or ablate a portion of the disc material. This reduces intradiscal pressure and decompresses nerve roots, leading to pain relief.
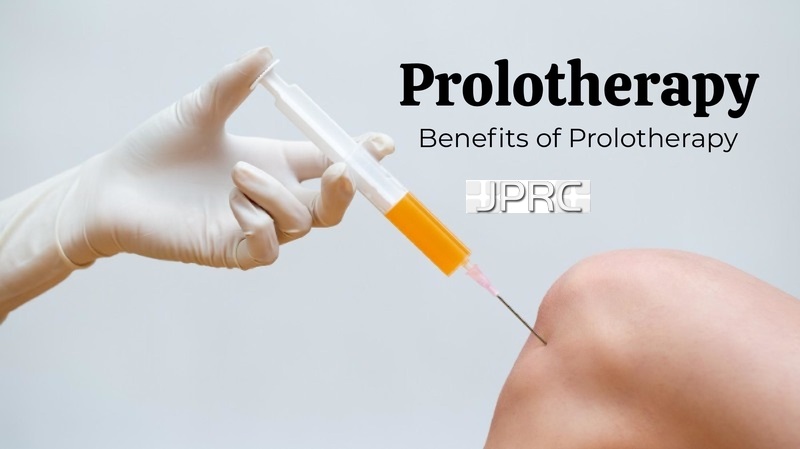
3. Intradiscal Injection Therapies:These include intradiscal steroid injections, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, or stem cell therapy. These injections target inflammatory mediators or promote tissue regeneration within the disc, thereby reducing pain and improving disc health.
Considerations:
1. Patient Selection: Proper patient selection is crucial, considering factors such as the extent of disc degeneration, presence of disc herniation, and responsiveness to conservative treatments.
2. Risk-Benefit Assessment: Each intervention carries potential risks, including infection, nerve injury, or worsening of symptoms. A thorough risk-benefit assessment should be conducted before proceeding with any procedure.
3. Multidisciplinary Approach: Intradiscal interventions are often part of a multidisciplinary pain management approach, which may include physical therapy, medication management, and behavioral interventions.
4. Long-term Outcomes: While intradiscal interventions can provide significant pain relief in the short term, their long-term efficacy varies among patients. Regular follow-up and assessment of outcomes are essential to monitor the effectiveness of the intervention.
Conclusion:
Intradiscal pain intervention techniques offer promising options for patients suffering from disc-related pain who have not responded to conservative treatments. With careful patient selection, thorough risk assessment, and a multidisciplinary approach, these interventions can significantly improve pain and function in eligible individuals.
This write-up provides an overview of intradiscal pain intervention techniques, considerations, and their role in comprehensive pain management strategies.






































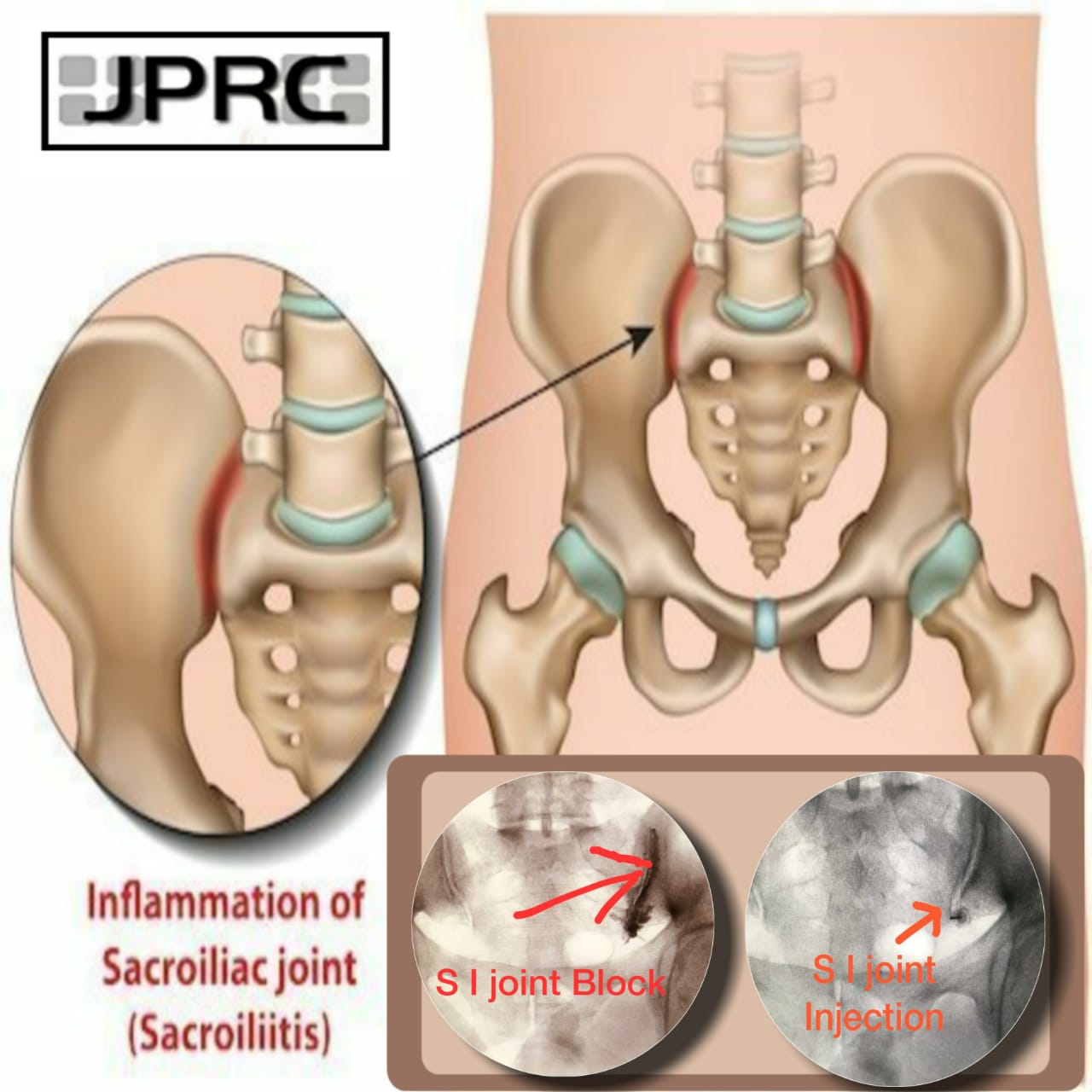




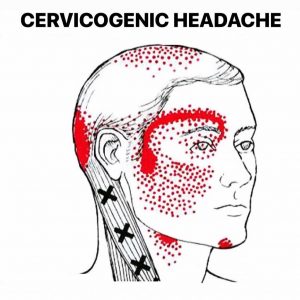




.jpg)








_Injection_Description_in_Hindi.jpg)













.jpg)







.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)










2.jpg)
3.jpg)
4.jpg)
1.jpg)
2.jpg)
5.jpg)
6.jpg)


7.jpg)
2.jpg)

8.jpg)

9.jpg)
3.jpg)

10.jpg)

11.jpg)


12.jpg)
4.jpg)